Domestic violence is a serious crime that affects countless families each year. While it can take many forms—emotional, physical, psychological, and even financial—the legal consequences of domestic violence are often misunderstood. One key question people have is whether domestic violence is classified as a felony. Understanding this legal classification can help victims and those accused of domestic violence navigate the legal system more effectively. In this blog, we’ll explore when domestic violence is classified as a felony and what factors can influence this decision.
What Is Domestic Violence?
Domestic violence refers to a pattern of abusive or threatening behavior used by one person to exert control over another in an intimate or familial relationship. This type of abuse occurs in various forms and can affect individuals regardless of age, gender, or socioeconomic status. Relationships commonly involved in domestic violence include spouses, intimate partners, parents and children, and other family members. Domestic violence is not limited to physical harm but encompasses a broad range of abusive actions designed to manipulate, intimidate, or cause fear in the victim.
Forms of Domestic Violence
- Physical Abuse: This involves the use of physical force against another person, resulting in injury or harm. Acts of physical abuse may include hitting, slapping, choking, shoving, or using a weapon to inflict harm. Even the fear of physical assault constitutes domestic abuse.

- Emotional and Psychological Abuse: This form of abuse involves actions intended to manipulate, belittle, or psychologically harm the victim. Emotional abuse can include constant criticism, threats, name-calling, humiliation, and controlling behavior. Over time, it can damage a person’s self-esteem and mental health.
- Sexual Abuse: This occurs when one person forces or coerces another into unwanted sexual activity. Sexual abuse in domestic violence scenarios may include rape, sexual assault, or forcing a spouse to engage in sexual actions without consent. Sexual coercion and threats of sexual violence also fall under this category.
- Stalking and Harassment: Stalking is a form of harassment in which the abuser repeatedly follows, monitors, or communicates with the victim to intimidate them. It can involve unwanted calls, texts, showing up uninvited, or using surveillance to control the victim’s movements and activities.
- Financial Abuse: This form of domestic violence occurs when one person controls another’s access to financial resources, making it difficult for them to leave the relationship or maintain independence. Examples include withholding money, limiting access to bank accounts, or preventing the victim from working or pursuing education.
The Impact of Domestic Violence
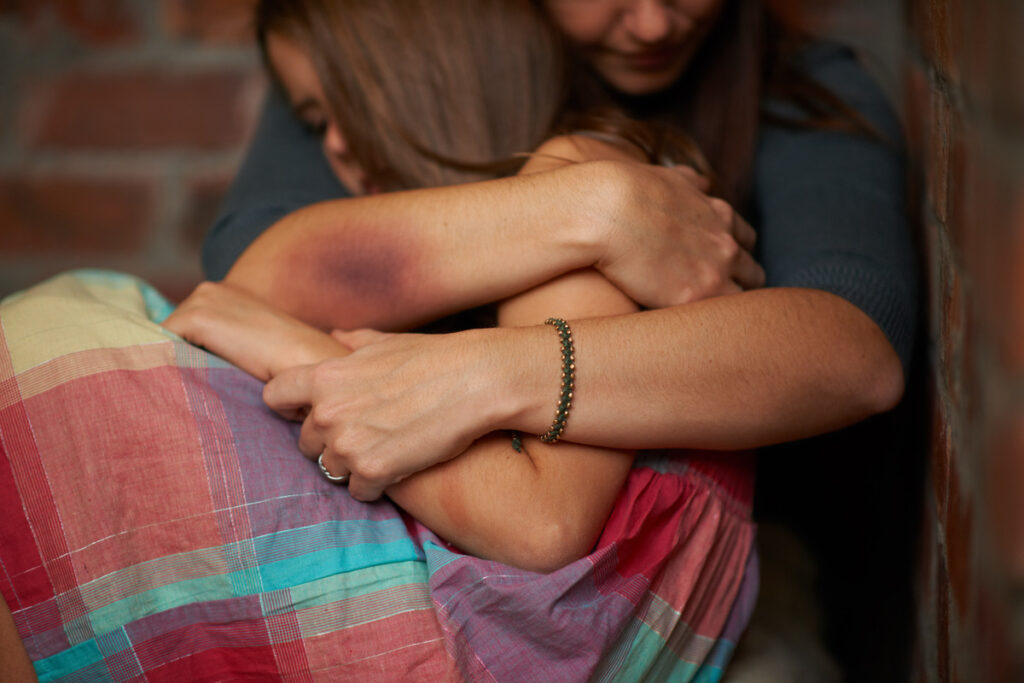
Domestic violence not only affects the immediate victim but can also have lasting consequences on families, children, and communities. Victims often suffer from long-term physical injuries, emotional trauma, and mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Children who witness domestic violence are more likely to experience developmental challenges and may carry the psychological scars into adulthood.
Legal Response to Domestic Violence
Many states, including Texas, have strict laws in place to address domestic violence. Law enforcement and the legal system work to protect victims by issuing protective orders, prosecuting offenders, and imposing penalties based on the severity of the crime. Domestic violence can result in charges ranging from misdemeanors to felonies, depending on the circumstances of the abuse. Additionally, repeat offenders and those who cause serious injury to their victims face harsher legal consequences.
Domestic violence is a pervasive issue that involves various forms of abuse aimed at controlling or harming individuals in intimate or familial relationships. Whether it involves physical, emotional, sexual, or financial harm, domestic violence leaves deep scars on victims and their families. Recognizing the different forms of abuse and understanding the legal ramifications can empower victims to seek help and hold offenders accountable. States like Texas take domestic violence seriously, with penalties designed to protect victims and deter future abuse.
Is Domestic Violence a Felony or a Misdemeanor?
Domestic violence can be classified as either a felony or a misdemeanor, depending on various factors, including the severity of the abuse, prior convictions, and whether a weapon was used during the incident.

- Misdemeanor Domestic Violence: In most first-time offenses or less severe cases, domestic violence may be classified as a misdemeanor. This typically applies when there is no significant physical injury, and the crime is not part of a pattern of repeated abuse.
- Felony Domestic Violence: Domestic violence is classified as a felony in more serious cases. For example, if the victim suffers severe injuries, if the offender has prior domestic violence convictions, or if a deadly weapon was involved, the charges can be elevated to a felony.
Factors That Make Domestic Violence to a Felony
Several factors can turn a misdemeanor domestic violence charge into a felony:
- Severity of the Injuries: If the victim sustains severe physical harm, such as broken bones, permanent scarring, or life-threatening injuries, the charges are more likely to be upgraded to a felony.
- Use of Weapons: When a weapon, such as a firearm or knife, is used to threaten or harm the victim, the case is typically treated as a felony.
- Prior Convictions: Repeat offenders are more likely to face felony charges. If the accused has a history of domestic violence or other violent crimes, their punishment may be harsher.
- Violation of Protective Orders: Violating a restraining or protective order during an act of domestic violence can lead to felony charges, even if the incident itself might have been considered less severe.
- Presence of Children: If a child witnesses the abuse or is harmed during the incident, the offender could face felony charges due to the added psychological trauma inflicted on minors.
Legal Consequences of Felony Domestic Violence
When domestic violence is charged as a felony, the legal consequences are much more severe compared to misdemeanor cases. These may include:

- Longer Jail or Prison Sentences: Felony convictions carry harsher penalties, which can include multiple years in state prison.
- Higher Fines: The financial penalties for felony domestic violence are significantly higher than those for misdemeanor offenses.
- Restraining Orders: Courts may issue long-term protective orders that prohibit contact with the victim.
- Loss of Rights: A felony conviction can result in the loss of certain rights, such as the ability to own firearms or vote.
- Impact on Custody: Felony domestic violence charges can severely impact a parent’s custody and visitation rights, especially if children were involved in the incident.
The Importance of an Attorney in Domestic Violence Cases
The role of an attorney in domestic violence cases is crucial for both victims and the accused. Domestic violence cases are complex and emotionally charged, often involving legal, emotional, and safety concerns. Whether you are seeking protection from an abuser or defending yourself against accusations, having legal representation is critical. Here are key reasons why an attorney is essential in domestic violence cases:

Guidance Through Legal Procedures:
Domestic violence cases involve a range of legal procedures, including filing protective orders, attending hearings, and navigating the criminal justice system. An attorney can guide victims and defendants through these processes, ensuring that all necessary paperwork is filed correctly and on time. They also ensure that you understand your legal rights at each stage.
Obtaining Protective Orders:
Victims of domestic violence often need immediate protection. An attorney can assist victims in obtaining protection or restraining orders to prevent the abuser from contacting them or their children. These orders may prohibit the abuser from contacting the victim, visiting their home or office, or engaging in abusive behavior. Legal expertise ensures the protective order is enforceable and effectively safeguards the victim.
Defending Against Criminal Charges:
For those accused of domestic violence, the consequences of a conviction can be severe, including jail time, fines, and a permanent criminal record. An experienced attorney can defend their client by analyzing evidence, challenging allegations, negotiating plea deals, or representing the defendant in court. Proper legal defense is critical in ensuring that the accused receives a fair trial and, if possible, avoids harsh penalties.
Child Custody and Divorce:
In cases involving domestic violence, legal matters often extend beyond criminal charges to family law issues, such as child custody, visitation rights, and divorce proceedings. An attorney can help victims secure custody of their children, ensuring that their safety and well-being are prioritized. Additionally, in divorce cases, an attorney can ensure that the abuse is factored into the division of assets and alimony.
Negotiating Settlements or Plea Deals:
In some cases, domestic violence charges can be resolved outside of court through negotiated settlements or plea deals. An attorney can negotiate on behalf of their client to reduce charges or avoid a trial altogether. For victims, this might involve securing compensation or favorable terms in family law cases, while for defendants, it could mean reduced sentencing or alternative penalties.
Providing Emotional Support and Advocacy:
Domestic violence cases are emotionally draining, and victims often feel isolated, confused, and scared. Attorneys act not only as legal representatives but also as advocates for their clients’ best interests. For victims, they provide emotional support and ensure their voices are heard. For defendants, they ensure their side of the story is fully represented in court.
Ensuring Fair Treatment in Court:
In cases where domestic violence escalates to criminal charges or civil lawsuits, attorneys ensure that the victim or defendant is treated fairly. They present evidence, cross-examine witnesses, and work to ensure the judge or jury hears all relevant facts. This is especially important for those facing false accusations, as skilled legal representation can expose weaknesses in the prosecution’s case.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Domestic violence can be classified as either a misdemeanor or a felony, depending on the severity of the abuse, use of weapons, and prior criminal history. Understanding this classification is important for both victims seeking protection and individuals accused of domestic violence. If you or someone you know is experiencing domestic violence, it is critical that you get legal help. A qualified attorney can help you navigate the complexities of these charges and ensure that your rights are protected.

If you’re dealing with a domestic violence case or have questions about its legal classification, reach out to a legal professional from Bobbie Young Law for guidance.
Your Legal Solution Starts Here
Clear, practical legal advice you can count on when it matters most