What Is Guardianship?
Parental Rights: A Fundamental Right

- Upbringing: Parents have the right to determine how their children are raised. This includes choices related to religious beliefs, cultural practices, moral guidance, and overall lifestyle. Parents are entrusted to instill values, discipline, and provide an environment they deem appropriate for the child’s growth and development.
- Education: Parents have the authority to decide where and how their children will be educated. This includes selecting public, private, or homeschooling options, as well as decisions regarding extracurricular activities, academic support, and overall involvement in the child’s educational progress.
- Health: Parents hold the right to make medical decisions on behalf of their children. This includes consenting to medical treatments, choosing healthcare providers, deciding on vaccinations, and making decisions about surgeries or other necessary medical procedures. Parents are expected to act in their child’s best interest when it comes to their health and well-being.
- Abuse: When there is evidence that the parent is physically, emotionally, or sexually abusing the child, the state can intervene to remove the child from the parent’s custody temporarily or permanently. The goal is to protect the child from immediate harm.
- Neglect: If a parent fails to provide the necessary care, such as adequate food, shelter, education, or medical attention, the state can take action to safeguard the child. Neglect cases often involve children living in unsafe conditions or without basic necessities.
- Abandonment: In situations where a parent has willfully abandoned their child, either by leaving them without care or failing to maintain a relationship with the child, the state may intervene to assign custody or guardianship to another individual or agency.
Emergency Situations and the Role of Guardianship
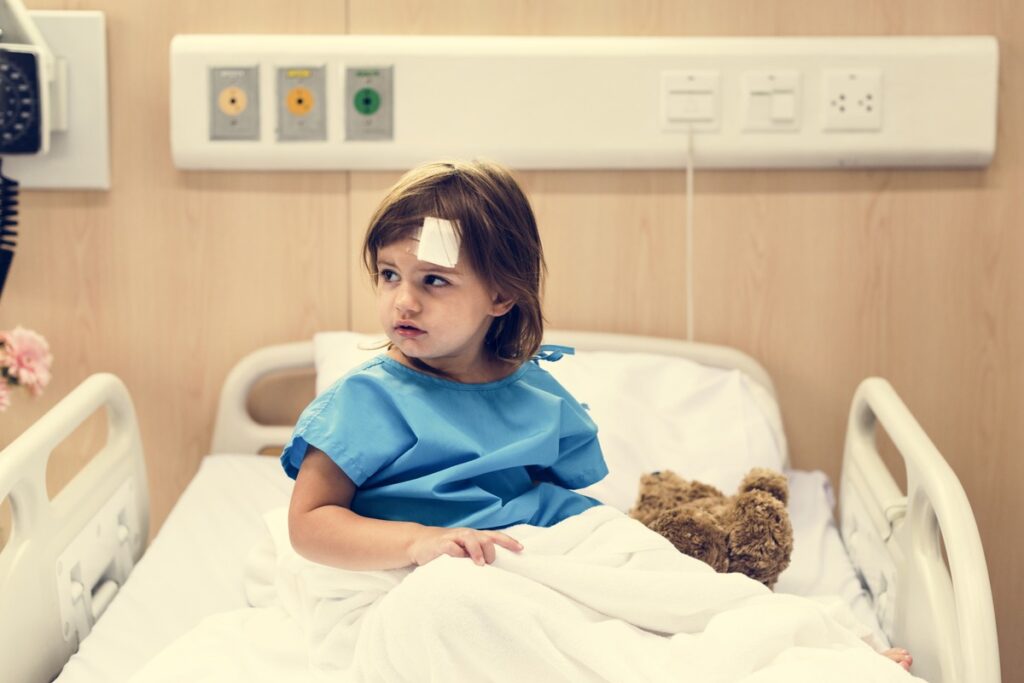
- Medical Emergencies: If a child is in immediate need of medical attention, a court may grant a temporary guardian the authority to make medical decisions, especially if the parents are unavailable or unwilling to consent to necessary treatment. In such cases, the court prioritizes the child’s health and safety over parental decision-making.
- Abuse or Neglect: If a child is in immediate danger due to abuse or neglect, the state can temporarily remove the child from the parents’ custody and place them under the care of a guardian. This can be done swiftly through an emergency court order. While parental rights are not permanently terminated in these cases, they are temporarily overridden to protect the child.
- Absentee or Incapacitated Parents: If parents are unable to fulfill their responsibilities, for example, if they are incarcerated, hospitalized, or missing, the court can appoint a temporary guardian to make necessary decisions for the child’s welfare. While the parent retains their legal rights, the guardian may act on the child’s behalf until the parents can resume their responsibilities.
Court’s Role in Balancing Guardianship and Parental Rights
Temporary Nature of Guardianship

Determining the Child’s Best Interests

The court’s primary focus is the child’s best interests, which may occasionally lead to a temporary overriding of parental rights. For instance, in situations where a child is in immediate danger, such as cases of abuse or neglect, the court may appoint a guardian to protect the child.
Restoring Parental Rights
Guardianship is not necessarily a permanent arrangement. If the court determines that the circumstances leading to guardianship have changed—such as the resolution of a medical condition, improved living conditions, or the parents proving they are fit to resume their responsibilities—the guardianship can be revoked.
Conclusion
In conclusion, courts play a vital role in balancing guardianship and parental rights, ensuring that the child’s welfare remains the highest priority while also respecting the legal rights of parents.
Guardianship is typically used as a temporary measure in times of crisis or when parents are unable to fulfill their responsibilities, with the court’s focus always on what is in the best interests of the child.
Importantly, guardianship does not permanently override parental rights, and in many cases, these rights can be fully restored once the parent is deemed fit to resume their role. The court’s involvement provides a careful review of each unique situation, striving to protect the child without unnecessarily infringing on parental authority.

Call to Action
Your Legal Solution Starts Here
Clear, practical legal advice you can count on when it matters most